Business corporations – meaning
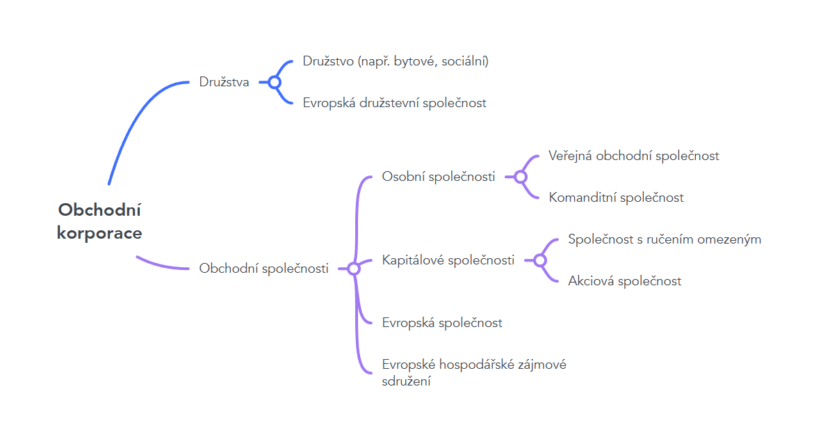
A business corporation includes all business corporations and cooperatives. Business corporations are further subdivided into partnerships (comprising a general partnership and a limited partnership), limited liability companies (comprising a limited liability company and a public limited company), European companies and European Economic Interest Groupings. Cooperatives then include either classic cooperatives, which can take many forms, and the European Cooperative Society.
The difference between a firm and a corporation: the term business corporation is often confused with the term firm. However, there is a significant difference between the two. Unlike a business corporation, a firm is not a legal entity, but merely the name under which the entrepreneur conducts its business and under which it is registered in the commercial register. Thus, every business corporation has a firm (name), but not every firm is a business corporation.
How a company and a cooperative differ
Commercial companies and cooperatives differ in several fundamental ways:
Purpose and focus
Business corporations are primarily focused on generating profits for their owners. Income is distributed according to the shareholdings of the partners or shareholders.
Cooperatives, on the other hand, are oriented towards meeting the needs of their members and communities. Although they may be in business, their profits are usually used to further the development of the cooperative or distributed according to the rules set out in the statutes.
Establishment and legal form
A company may be formed by two or more persons (or one person in the case of an Ltd. or an A.S.) and is created by registration in the commercial register.
A cooperative must have at least three founders who are also the first members of the cooperative. Like a company, it must be registered in the commercial register.
Are you solving a similar problem?
Are you dealing with registration in the commercial register?
We will be happy to help you. We have extensive experience with registrations in the Commercial Register. Everything is done simply, online, tailored to what you need and at a predetermined price. We can handle most cases within two working days.
I want to help
- When you order, you know what you will get and how much it will cost.
- We handle everything online or in person at one of our 6 offices.
- We handle 8 out of 10 requests within 2 working days.
- We have specialists for every field of law.
Ownership and decision-making
Commercial companies can be owned and managed by natural or legal persons. Assets and income are distributed among the owners according to their shareholdings.
A cooperative is owned by members who share not only ownership but also decision-making powers. The democratic principle of ‘one member, one vote’ is typical , regardless of the amount of the contribution.
Liability and responsibility
For companies, the level of liability depends on the type of company. For example, in a public company, the members are liable for all their assets. In contrast, a limited liability company and a public limited company have limited liability – the partners or shareholders are not liable for the company’s obligations beyond their contribution.
Co-operatives as a whole are liable with their assets, while individual members are not personally liable for its obligations.
Now let’s take a closer look at the different types of cooperatives and business corporations:
Types of cooperatives
Most of us probably think of an apartment building and neighborhood meetings when we think of a cooperative, but it is a much broader term than a traditional housing cooperative. A cooperative is a community of an unenclosed number of persons whose main purpose is to provide for the needs of its members.
Co-operative
A cooperative must be formed by at least three members. It is formed by a constituent meeting where the statutes – the basic document governing the internal functioning of the cooperative – are approved and officially established by registration in the commercial register.
Tip for article
Are you setting up a housing cooperative? We will draw up or check the statutes and make sure they comply with the law.
Both natural and legal persons can be members of the cooperative. For natural persons, the condition is the completion of compulsory schooling and reaching the age of 15. Founding members acquire membership automatically on the date of formation of the cooperative, while others may become members at any time during the cooperative’s existence by submitting a written application and having it approved by the cooperative.
The cooperative has three basic bodies:
- Members’ Meeting – the highest body, where each member has one vote.
- Board of Directors – manages the cooperative and represents it externally.
- Control Commission – supervises the activities of the Board of Directors and the management of the cooperative.
A cooperative can take different forms depending on its focus. The most typical types of cooperatives you may come across include:
- Housing cooperative: A housing cooperative is used to provide housing for its members. It owns a block of flats or other properties and individual members have user rights to the flats, not ownership rights.
- Social cooperative: Social cooperatives focus on employing and supporting disadvantaged people such as the disabled, the long-term unemployed or the elderly.
- Credit unions: Also known as credit unions or credit unions, these cooperatives provide financial services to their members, such as loans or savings.
European Cooperative Society
A European Cooperative Society is a transnational form of cooperative society that allows business and cooperation between members from different countries of the European Union. It can be formed by merging existing cooperatives, by converting a cooperative or as a newly established company.
Types of companies
Commercial companies are legal entities that are primarily used to conduct business and generate profits for their owners (members or shareholders).
Commercial companies include partnerships (public limited companies and limited partnerships), limited liability companies (limited liability partnerships and public limited companies), European companies and European Economic Interest Groupings.
Let’s look at the different types of companies in more detail:
Partnerships
Partnerships are characterised by the personal participation of the partners in the business and management of the company. The shareholders do not have a deposit obligation but are liable for the company’s obligations with all their assets.
A public company
A public company (v.o.s.) consists of at least two partners who run the business together and are liable for the company’s obligations with all their personal assets.
Basic characteristics of a public limited company:
- Minimum number of partners – must be at least two.
- Liability for liabilities – the partners are liable with all their personal assets.
- Management of the company – each shareholder has the right to participate in the management.
- Minimum capital – not set by law.
- Incorporation – it is established by signing the articles of association and entering them in the commercial register.
- Profit and loss – is shared equally between the shareholders, unless otherwise agreed.
Limited partnership
A limited partnership (limited liability company) combines elements of both partnerships and limited liability companies. There are two types of shareholders, who differ in their level of responsibility and right to manage the company:
- General partners – are liable for the company’s obligations with all their personal assets and have the right to manage the company. General partners usually receive remuneration for managing the company.
- Limited partners – are liable only to the extent of their outstanding contribution and cannot interfere in the management of the company. Limited partners receive a share of the profits according to the amount of their contribution.
Basic characteristics of limited liability companies:
- Minimum number of partners – at least one general partner and one limited partner.
- Liability – general partners are liable for their entire assets, limited partners only up to the amount of their contribution.
- Management of the company – only general partners have the right to manage the company
- Minimum capital – the law does not provide for a minimum capital, but the limited partner must make a deposit specified in the partnership agreement.
- Profit – profit is divided in half between limited partners and general partners. The general partners then divide the profits equally (unless otherwise provided in the partnership agreement).
Limited partnerships
Limited partnerships are based on the capital contribution of the partners and their liability is limited to the amount of their contribution. This means that the shareholders are not liable for the debts of the company with their personal assets.
Limited liability company
A limited liability company (s.r.o.) is a capital company in which the partners are liable for the company’s obligations only up to the amount of the outstanding contribution. This means that the partners are not liable with their personal assets. It is the most common type of commercial company in the Czech Republic.
Basic characteristics of an LLC:
- Minimum number of partners – 1 (can be one natural or legal person).
- Liability for liabilities – the partners are liable only up to the amount of the outstanding deposit.
- Minimum capital – the law provides for a minimum share capital of CZK 1, but in practice it is usually higher.
- Management of the company – the company is managed by a managing director or several managing directors.
- Profit share – shareholders are entitled to a share of profits according to their business shares.
- Incorporation of the company – it is established by signing the incorporation document and entering it in the Commercial Register.
Tip for article
Are you planning to set up an LLC? We will guide you through the process of setting up a company and offer you all the services you need for your business.
Joint stock company
A joint stock company (a.s.) differs from other forms of business in that it is divided into shares. The shareholders(shareholders) are not liable for the obligations of the company, they only risk the loss of the value of their shares. A public limited company can be private or public – public limited companies can trade their shares on the stock exchange.
Basic characteristics of a.s.:
- Minimum number of shareholders – can be formed by one person (natural or legal).
- Liability – shareholders do not guarantee personal assets, they only risk the loss of invested capital.
- Minimum share capital – CZK 2 000 000 (or EUR 80 000 if a publicly traded company).
- Management of the company – the statutory body is the board of directors or the statutory director (depending on the chosen management system).
- Profit sharing – shareholders receive dividends if the company decides to pay them.
- Share trading – can be private (shares not publicly traded) or public (shares traded on an exchange).
European society
A European company is a multinational form of public limited company that allows business in all member states of the European Union and the European Economic Area under a single legal framework.
The basic characteristics of a European Company are:
- Legal personality – A European company is a legal entity with its own legal personality.
- International scope – allows for easy transfer of the registered office to another Member State without liquidation.
- Share capital – minimum of EUR 120 000.
- Shareholder liability – shareholders are not liable for personal assets, only up to the amount of their shareholding
- Corporate governance – choice between dualist or monist governance.
- Registration – the SE must be registered in the commercial register of the Member State where it has its registered office.
European Economic Interest Grouping
A European Economic Interest Grouping (EEIG) is a specific legal form allowing companies or sole traders from different EU countries to work together on joint projects without losing their legal autonomy.
The main objective of an EEIG is not to generate profit, but to promote and facilitate cross-border cooperation between its members. If an EEIG generates a profit, this profit is distributed among the members and taxed in their home countries.
Basic characteristics of an EEIG:
- It is not a separate legal entity – but it has legal personality, can conclude contracts and can appear before the courts.
- It is not for profit – its main purpose is to promote the business of its members.
- Minimum number of members – at least two members from two different EU Member States.
- Liability of members – members are jointly and severally liable for the obligations of the EGTC.
- Tax transparency – the association itself does not pay taxes, profits are distributed among members and taxed by them.
Summary
Business corporations include partnerships and cooperatives. Business corporations are divided into partnerships (limited liability companies, limited liability partnerships) and limited liability companies (limited liability companies, limited liability companies), while there are also European forms such as the European Company (SE) and the European Economic Interest Grouping (EEIG). Cooperatives include traditional cooperatives and the European Cooperative Society.
Commercial companies are profit-oriented, while cooperatives meet the needs of members. Partnerships haveunlimited liability of the members, while limited companies are liable only up to the amount of the contribution.
In a general partnership , all partners are liable with their entire assets, while in a limited partnership , general partners are liable with their entire assets and limited partners are only limitedly liable. A limited liability company is the most common form of business with limited liability for the outstanding deposit, while a joint stock company is divided into shares and may be publicly traded.